Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. It is a lifelong and chronic condition that stops your body from using insulin the right way and alters the way your body processes sugar (known as glucose), which is an important source of energy. When you have type 2 diabetes, your body is resistant to insulin or your body does not produce enough insulin needed to maintain normal glucose levels. Insulin is a hormone that allows glucose in the blood to enter cells and keeps blood sugar level from getting too high or too low. This type of diabetes was known as adult-onset diabetes, however, nowadays more and more children are diagnosed with this disease. It is said that it is due to the rising number of childhood obesity.
The symptoms and signs of type 2 diabetes usually develop slowly. Some people are not aware that they have type 2 diabetes for years. Here are the signs you should be aware of:
- Extreme thirst
- Frequent urination
- Increased hunger
- Blurry vision
- Sudden, unintended weight loss
- Fatigue
- Infections that happens frequently
- Numbness in the hands or feet
- Wounds or sores that heal slowly
If you notice any of the symptoms, it is best to call your doctor immediately so your doctor can diagnose your condition properly and you can get early treatment.

Type 2 diabetes occurs when your body resists insulin and when your pancreas cannot produce enough insulin. When there is not enough insulin in your body, sugar builds up in your bloodstream instead of moving to your cells. It is still mainly unknown why this condition can happen. However, it is believed that genetics and environmental factors contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. Factors that can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes are:
- Family history, your chance of getting type 2 diabetes increases if you have a family member, mainly a parent or a sibling who has type 2 diabetes.
- Race, it is still unclear why, but people from certain races are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, including Asian-American, American Indian, black, and Hispanic.
- Weight, even though you do not have to be overweight to have type 2 diabetes, people who are overweight have a higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Inactivity, physical activity can help you control your weight and makes your cells become more sensitive to insulin.
- Age, as you get older, particularly after you reach the age of 45, your risk of developing type 2 diabetes is higher.
- Too much glucose from the liver, your liver usually sends out glucose when your blood sugar is low and then stores it when your blood sugar is high, but some people’s liver keeps sending out glucose.
Many people ignore the signs of type 2 diabetes, especially when it is still in its early stage. However, diabetes can affect numerous major organs. Long-term complications can eventually be life-threatening. Diabetes can lead to nerve damage, heart and blood vessel disease, kidney damage, hearing impairment, sleep apnea, skin conditions, eye damage, and slow healing.
Healthy lifestyle choices are one of the main factors to prevent type 2 diabetes and it can also help prevent complications even when you are already diagnosed with diabetes. Here are some examples of a healthy lifestyle:
- Eat more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid added sugar or food with a lot of fat and calories.
- Add at least 30 to 60 minutes of physical activity into your daily routine. Make time to take a walk, ride a bike, or swim.
- If you are overweight, try to lose 5% to 10% of your body weight and keep your weight in a healthy range.
Although type 2 diabetes is a lifelong condition and there is currently no cure for it, your life does not have to end with it because there are many ways to manage it so you can stay healthy. Most people can manage the condition by having the right diet plan and fitness routine. A healthy diet can help you feel better. Focus you’re eating plan around food with fewer refined sweet, calories, and foods that contain saturated fats. Eat more vegetables, fruit and more foods that contain fiber. Being physically active is one of the key parts of managing your diabetes type 2. You can do anything you like, such as walking, cycling, or swimming you do not have to become a marathoner, all you need to do is find the activity you like, get moving, and do it regularly.
You may also want to check your blood sugar level regularly, especially if you are on insulin therapy. This will help you to know if your blood sugar level stays within your target range.
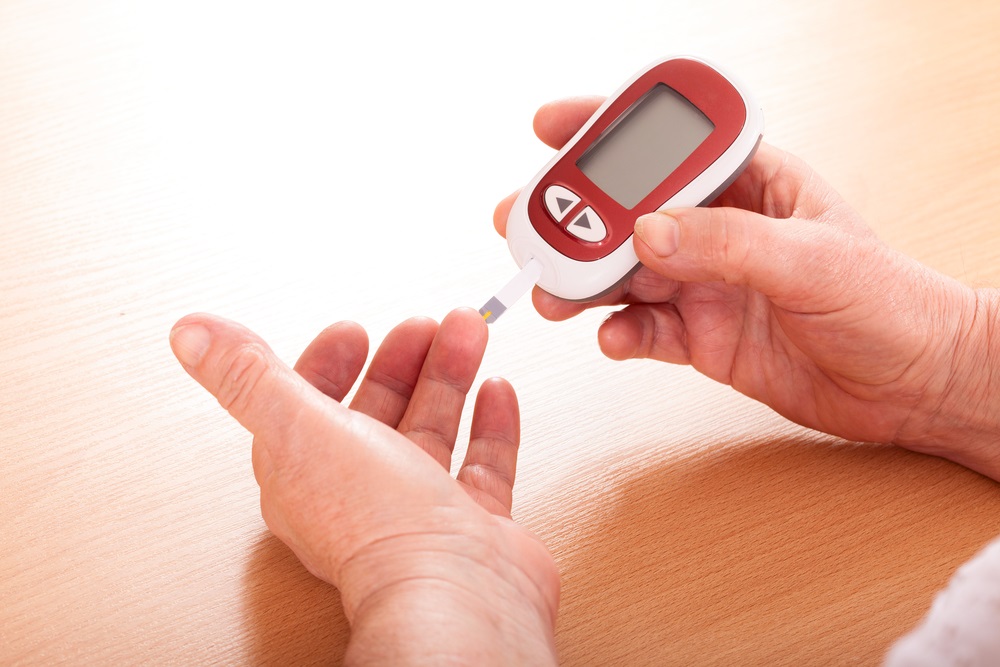
While some people can manage type 2 diabetes with exercise and diet, others may need insulin therapy and diabetes medications. There are numerous factors that determine which medication is best for you, such as your blood sugar level and your health condition (if you have any other health problems). Some of the most common medications for type 2 diabetes are metformin, sulfonylureas, meglitinides, thiazolidinediones, DPD-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, as well as insulin. Insulin therapy is typically used as the last resort, but today many doctors prescribe it sooner because of its benefits.
If you have type 2 diabetes and you are overweight (or your body mass index is higher than 35), you may be advised to undergo bariatric surgery (weight-loss surgery). People who had bariatric surgery seen dramatic improvements in their blood sugar levels. However, it is important to note that surgery has its drawbacks, such as risks, costs, and drastic lifestyle changes.
Other than taking medications, having therapy, and surgeries, you also need to make some lifestyle changes. For instance, you need to schedule an annual physical exam, take care of your teeth, pay attention to your feet, keep your blood pressure under control, quit smoking, and keep your vaccinations up to date. Remember that you need to commit to managing your diabetes to stay healthy and avoid further complications.
